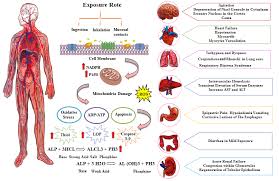
𝗧𝗛𝗘 𝗔𝗕𝗖𝗗𝗘 𝗢𝗙 𝗛𝗘𝗣𝗔𝗧𝗜𝗧𝗜𝗦
Hepatitis A (Infectious Hepatitis)
🟣 Cause: Hepatitis A Virus (HAV)
🟣 Transmission: Feco-oral route
This means the virus is shed in feces and enters the body through ingestion (e.g., contaminated food or water).
🟣 Risk factors: Poor sanitation, contaminated food/water, close contact with an infected person
🟣 Vaccine: Available
🟣 Chronic infection: No
🟣 Severity: Usually mild and self-limiting
Hepatitis B (Serum Hepatitis)
🔴 Cause: Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
🔴 Transmission: Bodily fluids
Blood, semen, vaginal fluids, saliva, from mother to baby during childbirth.
🔴 Risk factors: Unprotected sex, needle sharing, blood transfusion, healthcare exposure
🔴 Vaccine: Available
🔴 Chronic infection: Possible
🔴 Complications: Cirrhosis, liver cancer
Hepatitis C
🟡 Cause: Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)
🟡 Transmission: Blood
Mainly through sharing needles or unscreened blood transfusion.
🟡 Risk factors: IV drug use, tattoos/piercings with non-sterile tools
🟡 Vaccine: None
🟡 Chronic infection: Very likely (more than 70 percent of cases)
🟡 Complications: Chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma
🟡 Note: Often asymptomatic until liver damage is advanced
Hepatitis D
🔵 Cause: Hepatitis D Virus (HDV), a defective virus
🔵 Dependency: Requires Hepatitis B for replication and activation
🔵 Transmission: Same as HBV (blood and body fluids)
🔵 Risk factors: Co-infection or superinfection with HBV
🔵 Vaccine: No specific vaccine, but HBV vaccine prevents HDV
🔵 Chronic infection: Possible
🔵 Complications: More severe liver disease than HBV alone
Hepatitis E
🟤 Cause: Hepatitis E Virus (HEV)
🟤 Transmission: Feco-oral route (same as Hepatitis A)
🟤 Risk factors: Contaminated water in endemic areas
🟤 Vaccine: Available in some countries
🟤 Chronic infection: Rare (except in immunocompromised individuals)
🟤 Complications: Dangerous in pregnant women (can be fatal in third trimester)